On February 12, 2022, the journal Bioinformatics published the “Multimodal reasoning based on knowledge graph embedding for specific diseases” online. This paper presents a complete construction and inference process of the multimodal specific disease knowledge graph. Doctoral students Zhu Chaoyu and Xia Xiaoqiong from Liu Lei's team are this paper's first and third authors. Professor Yang Zhihao and his doctoral student Li Nan (Dalian University of Technology) are the second and fourth authors. Professor Liu Lei and Associate Professor Zhong Fan are the co-corresponding authors.

Knowledge Graph (KG) is a way to store knowledge, it represents facts in the real world through a large number of triplets (head entity, relation and tail entity). KG is widely used in the biomedical field to predict drug-target interactions and adverse drug reactions, and also to construct clinical decision support systems.
Most existing biomedical KGs focus on a particular entity type, but few KGs focus on specific diseases. We consider 11 diseases in this work, including 5 cancers and 6 non-cancer diseases. After collecting relevant abstracts from PubMed by keywords, Yang Zhihao's team obtained the original triplets through named entity recognition and relationship extraction. SDKG-11 was constructed by fine-grained matching of entity and relation, which can represent the existing knowledge set of these specific diseases.
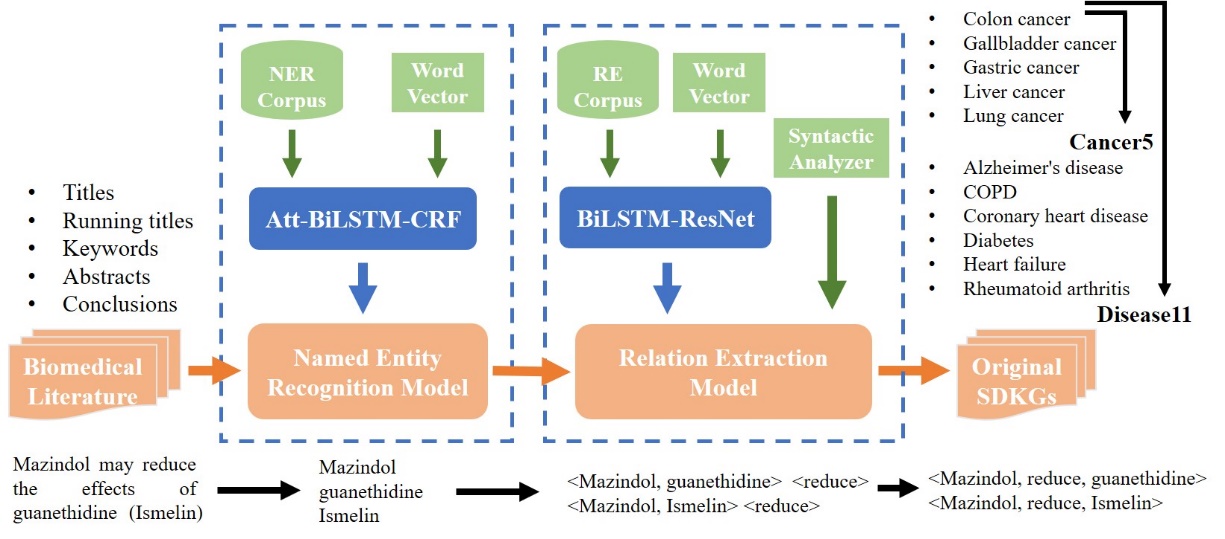
Since new biomedical knowledge is being presented every day, almost all constructed biomedical KGs are incomplete. Therefore, reasoning new knowledge by the existing knowledge is a universal idea. Knowledge Graph Embedding (KGE) maps entities and relations into a low-dimensional vector space, using simple mathematical calculations instead of explicitly defining the reasoning process, which has recently emerged as a paradigm for KG reasoning. Liu Lei's team combined the embedding of three modals of KGE structure, category and description by the reverse-hyperplane projection to define the multimodal scoring function.
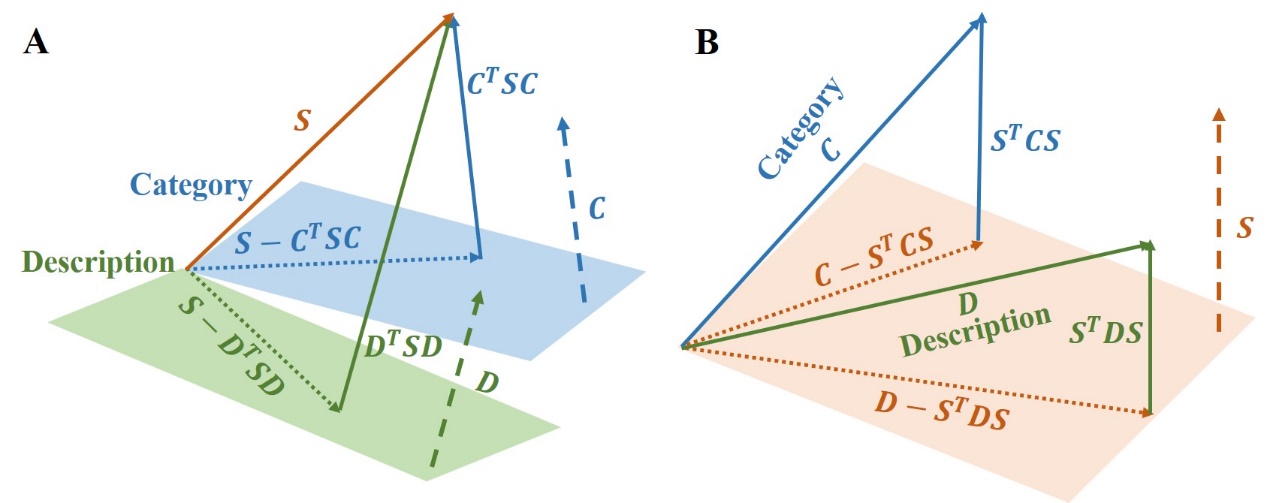
By defining a scoring function, they obtained the top-ranked drug-gene, gene-disease, and disease-drug pairs. They then verify the model’s reliability by manually proofreading predicted entity pairs. Using embedding results as initialization parameters for the biomolecular interaction classification, they demonstrate the universality of embedding models. This paper completed the multimodal reasoning for SDKG-11, wish to generate new knowledge sets that are valuable for scientific research and clinical decision making.